With the increasing acceptance of cryptocurrencies as viable and safe financial assets, and the rapidly growing number of crypto exchanges around the world, market making in the crypto space has become increasingly common, yet still largely unexplored.
Market makers play an important role in increasing the accessibility and liquidity of cryptocurrencies to traders, investors and market participants around the world. Market making is an activity whereby a trader simultaneously provides liquidity to both buyers and sellers in a financial market. Liquidity is the degree to which an asset can be quickly bought or sold without notably affecting the stability of its price.
In this post, we’ll elaborate on the benefits of crypto market making, explain what cryptocurrency market making is, and provide a basic guide on how to leverage the service.
What are the benefits of market making in the crypto space?
- Increases market liquidity and order book depth
- Reduces price volatility
- Assists with fair price discovery
- More efficient bid-ask spreads in cryptocurrency exchange order books
- More orderly entry and exits points for traders
- Dramatically reduces slippage
- Helps accommodate large institutional investors
- Mitigates dramatic price swings
What’s The State of the Cryptocurrency Market?
Before we go into the details of crypto market making, let’s first look at the current state of the cryptocurrency market.
The Crypto Market Is Still Fragmented
Crypto is still nascent and liquidity is still highly fragmented. Although the overall market has recently risen above the $1 trillion market cap, the market is still very young and in stages of early development. The vast majority of crypto liquidity is in Bitcoin and Ethereum markets. In comparison to other asset classes, crypto is still very small and is still too nascent for some major players to allocate big capital.
The Crypto Market Is Becoming More Institutional
Despite this fragmentation, many institutional companies and asset managers have been entering the crypto market. This is predominantly to buy the most liquid asset, Bitcoin. To buy a $500m position in Bitcoin, a firm must use an execution provider who will carry out the purchase algorithmically.
The purchase will be carried out through many exchanges and market makers over a longer period of time, if a $500m purchase was done through one trading venue it would have a massive impact on the wider market. The liquidity of Bitcoin is a major factor to consider when traditional investors are sizing up the asset class.
Token Ecosystems Are Small but Growing
Token ecosystems that are much smaller than Bitcoin have much less liquidity and are far more vulnerable to major market moves. Healthy order books are even more important to new and developing projects to ensure their order book is robust enough to accommodate larger traders and to help facilitate the growth of the wider token ecosystem. Currently Bitcoin and Ethereum are responsible for around 75% of 24hr market trading volume.
What Is Crypto Market Making?
Market Makers reduce friction and make a market liquid. In order for traders to be able to buy or sell large amounts of crypto assets, it is necessary for them to have access to an efficient market. A crypto market maker does nothing more and nothing less than facilitating tight markets by posting tighter spreads. In other words, crypto market makers like GSR facilitate the availability of crypto assets in the market.
Exchanges are the venue where traders gather, market markets provide the liquidity that is needed for tight order books, efficient price discovery and an efficient trading experience.
What is Liquidity?
Simply stated, the liquidity of an asset is its availability for buyers and sellers to easily trade it at any given time. Crypto market markets post an open “bid” price (price at which the market maker is willing to buy from traders) and an “ask” price (price at which the market maker is willing to sell to traders). Liquidity is the degree to which an asset can be quickly bought or sold without notably affecting the stability of its price.
Order Book Dynamics
For a given asset, the difference between the best bid and the best ask is called the bid-ask spread. Markets that have low liquidity will generally have wide bid-ask spreads in their order books. The size of the spread has a direct influence on the volume traded in the market, with a tighter spread generally resulting in more volume traded.
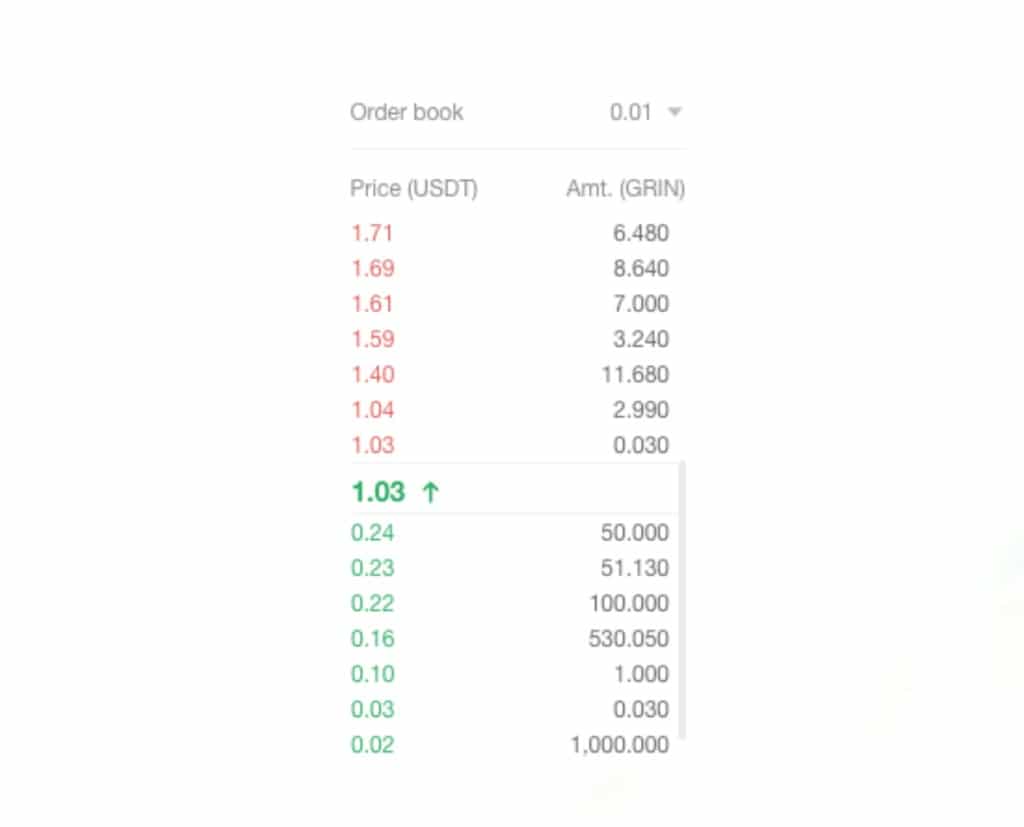
Source: coinall.com
In the above order book for GRIN/USDT on Coinall, traders are exchanging GRIN tokens for the stablecoin Tether (USDT). We can see a highly inefficient order book. The last offer to buy was $0.24c, and the last offer to sell was $1.03c, which is a drastic mismatch, and a market that is not functioning. The depth of the order book is also non-existent, with the top seven offers to buy showing extreme price difference, the smallest being $0.2c.
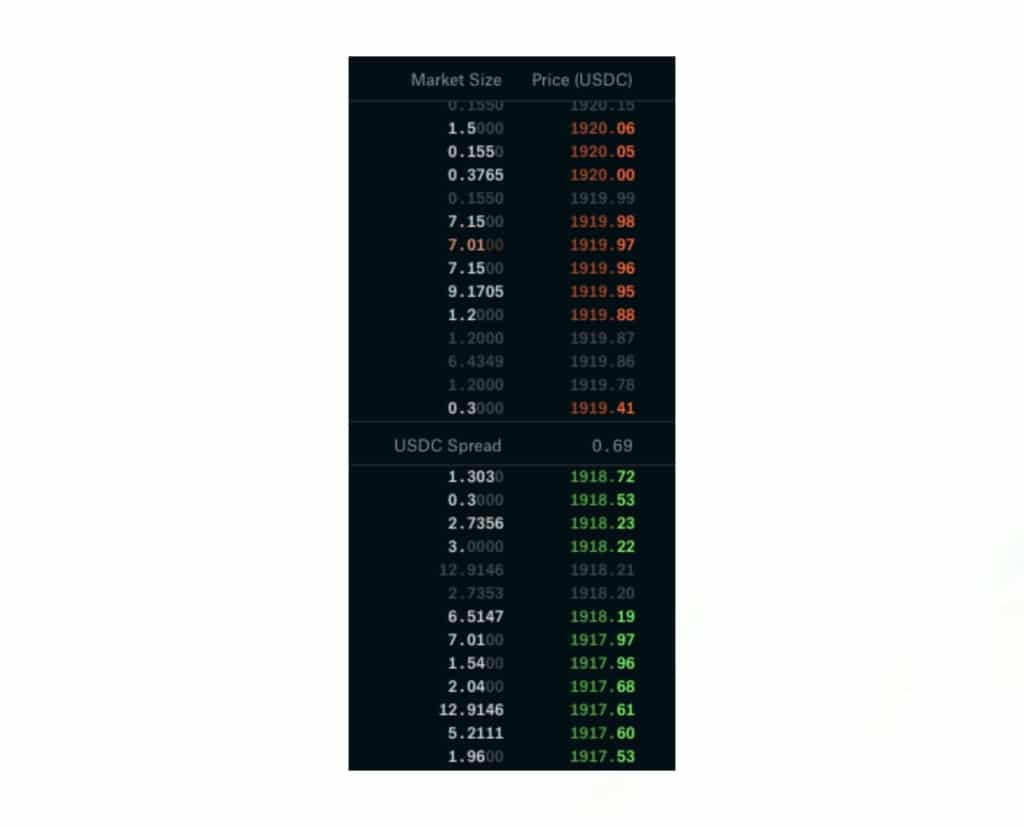
Source: Coinbasepro.com, a highly liquid order book and reputable exchange.
In comparison, here is the ETH/USDC market on Coinbase Pro where traders are exchanging Ethereum (ETH) for the popular stablecoin USDC. The first thing we notice is there is a $0.69 cent difference between the last bid and ask for an asset worth over $1,918. This is a liquid market that has a tight spread and depth in the order book (plenty of orders within $2 worth of USDC.)
Market reports that have unearthed suspicious trading activity across a vast number of exchanges have used methods that include website traffic analysis, monitoring of inconsistent volume activity, analysis of monotonic trading volumes, and analysis of questionable market cap to trading volume ratios. All of these techniques, including looking at the optics of an order book, help provide clarity into the health of an exchange or project. However, optics can be created by wash trading, allowing for order books to look far more liquid than they actually are. Timestamped data of an order book through an API connection is the only way to truly determine a platform or project’s trading activity. Overall, the crypto market is expanding rapidly, and there is a substantial list of reputable venues with good liquidity.
Why Are Market Makers Important?
Markets that have low liquidity will generally have wide bid-ask spreads in their order books that can increase the volatility of the asset. Therefore it makes it more difficult for traders to get a good price for their trade, and have their orders filled.
The overall liquidity of a market greatly influences its growth, and market makers play a big role in ensuring liquidity. Cryptocurrency markets are the only markets in the world that operate 24/7, therefore consistent liquidity is vital.
What Are the Benefits of Market Making in the Crypto Space?
There are a number of benefits to market-making in the crypto space, and for the traders that comprise the market. Let us examine them one by one.
Crypto Markets Are More Volatile Than Other Markets
Although one of the benefits that market makers bring to the market is better stability, cryptocurrencies are still relatively volatile, which means that there is generally a greater opportunity to make profits when compared to most other traditional financial markets, but also a greater risk to projects and traders. If a project doesn’t have enough healthy crypto markets on exchanges it can jeopardize the future of the market. Liquidity helps mitigate dramatic price movements and accommodates traders of all sizes to get in and out of positions during daily crypto volatility.
Healthy Order Books Facilitate Growth
Partnerships with market makers can result in KPIs around order book spread and depth, ensuring liquidity providers are held accountable for the overall health of the market and wider token ecosystem. The metrics are key factors crucial to the trading activity of an ecosystem and ensure orderly entry and exit points for traders, which also dramatically reduces the chance of slippage.
Accommodating Institutional Investors
Efficient order books help accommodate larger institutional investors. Highly liquid makers can absorb bigger market orders, without increasing volatility. Larger allocators want to ensure they get the best price for their assets, and market makers are a way of ensuring their experience is positive and efficient.
Ask us about your options in crypto market making now >
Reports, market reports, and other information (“Information”) provided by GSR or its affiliates have been prepared solely for informative purposes and should not be the basis for making investment decisions or be construed as a recommendation to engage in investment transactions or be taken to suggest an investment strategy in respect of any financial instruments or the issuers thereof. Information provided is not related to the provision of advisory services regarding investment, tax, legal, financial, accounting, consulting or any other related services and is not a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any asset. Information is based on sources considered to be reliable, but not guaranteed to be accurate or complete. Any opinions or estimates expressed herein reflect a judgment made as of the date of publication, and are subject to change without notice. Trading and investing in digital assets involves significant risks including price volatility and illiquidity and may not be suitable for all investors. GSR will not be liable whatsoever for any direct or consequential loss arising from the use of this Information. Copyright of this Information belongs to GSR. Neither this Information nor any copy thereof may be taken or rented or redistributed, directly or indirectly, without prior written permission of GSR. Not a solicitation to U.S. Entities or individuals for securities in any form. If you are such an entity, you must close this page. Trading from Singapore, please review The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) compliance note.